In the field of nuclear engineering, since the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on March 11, 2011, there has been a growing demand for monitors that can withstand severe accidents. As one example, devices are necessary for operations in reactor containment vessels at high temperatures of 300 °C with integrated doses of 5MGy of gamma-ray irradiation. The author of this review, Kaneko et al., have been working on the development of diamond γ-ray detectors and diamond FETs for the development of diamond radiation measurement systems for use in reactor containment vessels. The high temperature operation of 500 °C has been achieved by growing high purity diamond single crystal and reducing surface leakage current by guard ring. For radiation resistance of the diamond radiation detector, we have confirmed that the characteristics of the detector do not degrade even after γ-ray irradiation with an integrated dose of > 3 MGy.
In such a harsh environment, the entire radiation measurement system is also required to have radiation hardness and heat resistance. In order to satisfy these requirements, diamond FETs are under development. For radiation hardness and high temperature operation of the FETs, diamond MESFETs have been shown to operate stably at 10 MGy and 500 °C. Radiation hardened Hydrogen- terminated Diamond metal–oxide semiconductor FET (RADDFET), which enables higher transconductance than diamond MESFET and nearly temperature independent operations, were also stably operated after x-ray irradiation up to 1 MGy. Figure 1 shows drain current and drain voltage characteristics of diamond FETs after X-ray irradiation. Clear pinch-off characteristics were maintained after 1 MGy irradiation.
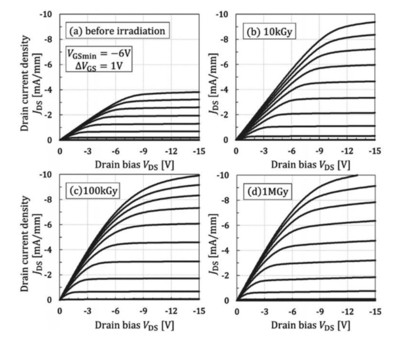
Figure 1. Drain current and drain voltage characteristics of RaDDFEt (a) before and (b) after 10 kGy, (c) 100 kGy, and (d) 1 mGy. after the mGy of X-ray irradiation, diamond FEts presents stable drain current and drain voltage characteristics. the figure is from Ref [72] copyright © 2020 aiP publishing.
Other applications in the nuclear engineering is the detection of alpha particles derived from nuclear fuel in nuclear fuel reprocessing plants. In the plants, the reprocessing process of nuclear fuel containing uranium melts under strong acid, which requires the measurement of alpha particles at temperatures above 100 °C. Since diamond is chemically stable, it is suitable for such applications because of its excellent corrosion resistance. Diamond radiation detectors also offer high temperature operation as mentioned above. It has been reported that polycrystalline diamond radiation detectors present long stability for this application.
CSMH masters the core process of MPCVD to prepare high-quality polycrystalline diamond wafer and realize mass production, and it is the first in the world to create an efficient and precise machining method for diamond atomic-level surface based on plasma-assisted polishing. The surface roughness of the diamond heat sink is reduced from tens of microns to below 1 nm, reaching the semiconductor-level application standard.
The company will invest heavily in R&D and innovation, continue to break through technical difficulties, and make continuous efforts to solve the bottleneck problem of heat accumulation in high-power density devices in the future.
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message