Pos:
Home KnowledgeTechnologyYYDS, diamond wafer is the ultimate heat sink material for semiconductor lasers!Compared with solid-state lasers, fiber lasers and other technologies, semiconductor lasers have a higher electro-optical conversion efficiency, up to 40% to 60%, even so that they will still produce a lot of heat when they work, such as poor heat dissipation effect and untimely heat dissipation, it will cause the chip temperature to increase - directly affecting the semiconductor laser output power, threshold current density, electro-optical conversion efficiency, differential quantum efficiency, polarization and other performance, and lead to a decline in the life and reliability of semiconductor lasers, and even damage the chip. Good heat dissipation is one of the key factors to ensure the power and beam quality of semiconductor lasers. Therefore, it is urgent to solve the heat dissipation problem of semiconductor lasers.
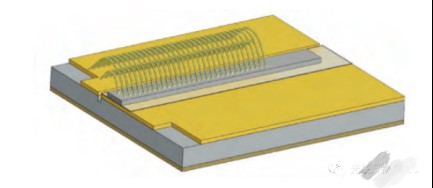
Figure 1 Semiconductor laser profile
The requirements of high-power semiconductor laser packaging for transition heat sink are mainly reflected in two aspects: low thermal resistance and low thermal mismatch - the higher the thermal conductivity of the transition heat sink, the more effective the laser thermal resistance can be reduced; At the same time, it is also necessary to consider the chip matching the coefficient of thermal expansion of the heat sink, select the appropriate sintered solder, reduce thermal mismatch, and thus ensure/improve the output characteristics of the laser.
j=-k(dT/dx). By Fourier's Law, there are:
R=h/KS
R is the thermal resistance, h is the thickness of the solder layer, K is the thermal conductivity, and S is the thermal conductivity in the direction of the vertical heat flow. Under the same other conditions, the thermal resistance of the laser is inversely proportional to the thermal conductivity, and the higher the thermal conductivity of the hot sink material, the more effective the thermal resistance of the device can be reduced.
Laser thermal resistance can be expressed as Rth, according to the thermal resistance definition: dissipation of units of thermal power caused by temperature rise, thermal resistance Rth can be expressed as follows:
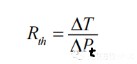
where ∆T is the active zone temperature rise and Pt is the thermal power.
The temperature rise in the active region of semiconductor lasers is not easy to measure, and can be calculated by the amount of wavelength drift ∆λ:

where λ (T ) is the wavelength drift coefficient.
The calculation formula for laser thermal power Pt is:

where P is the injected electrical power and Pop is the laser output power.
Thermal resistance Rth can be expressed as:

The calculation formula for laser junction temperature Tj is:
![]()
Where Ta is the heat sink temperature.
The thermal resistance of the laser is measured using the wavelength drift method. Taking the diamond heat sink as an example: the measured heat sink temperature is 20 °C, 25 °C, 30 °C, 35 °C, 35 °C, the laser wavelength under the condition of 10A operating current, the test results are shown in the following figure, and the wavelength drift coefficient of the device can be calculated to be 0.308 nm/°C.

Fig. 2 Wavelength change curve at different temperatures
When the heat sink temperature is set at 20°C, the laser output power, center wavelength and laser operating voltage under different current conditions are tested and recorded by formula

The thermal power of the laser under different current conditions can be calculated, and then the fitting curve of the relationship between the center wavelength of the laser and the thermal power of the laser can be obtained, as shown in the following figure, and the calculation can be obtained dλ/ dPt = 0.535nm/W.
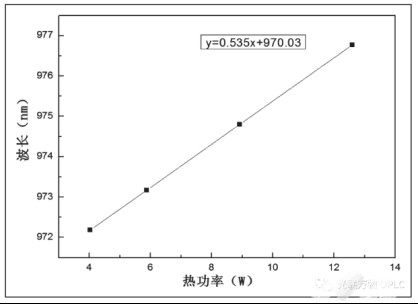
Figure 3 Wavelength vs laser thermal power relationship curve
by formula:
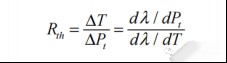
The thermal resistance of the available laser is 1.74°C/W (0.535/0.308).
by formula:

Calculate the chip junction temperature of 53.94°C when the resulting laser injection current is 25A.
The experiment used aluminum nitride heat sink as a transition heat sink package with 5 chips in the same batch, after the package is completed, the laser thermal resistance is tested in the same way, and the laser thermal resistance of the aluminum nitride heat sink as the transition heat sink package is 2.91 °C/W. Through data comparison, it can be obtained that some application areas require excessive heat sinking to use diamond, and its thermal conductivity thermal conductivity can reach 1000~2200W/(K·m), compared with the thermal conductivity of 140~230W/(K·m) aluminum nitride transition heat sinking, diamond heat sinking can significantly improve the laser heat dissipation effect.
CSMH is a high-tech enterprise focusing on the research and development and production of third-generation (wide bandgap) semiconductor substrate materials and devices, and is committed to becoming the world's leading wide bandgap semiconductor materials and devices company. We have always adhered to the concept of customer first, to provide customers with the best products and services. At present, the company has realized the large-scale production of diamond and aluminum nitride related products, the existing diamond wafer Ra < 1nm, diamond hot sink thermal conductivity of 1000-2000W/m.k, and more GaN on diamond, Diamond on GaN, diamond-based aluminum nitride and other products. And has been widely used in 5G base stations, lasers, new energy vehicles, new energy photovoltaics and other fields.
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message