When the LED chip is working, about 70 to 80% of the energy is converted into heat. With the increase of LED chip integration and power, the heating intensity of the unit area of the LED light source increases rapidly, and the excessive LED chip junction temperature not only makes the LED light source life decay sharply, but also causes a serious or even fatal impact on the peak wavelength, optical power, luminous flux and many other optical properties of the LED. Especially for high-power integrated LED light sources, due to the large heat generation and high concentration of heat in the LED light source, its heat dissipation problem is the primary consideration of LED development.
At present, the common LED heat dissipation materials on the market mostly use aluminum, plastic or ceramic and other profiles made of different processing processes. These heat sinks rely on the thermal conductivity of the radiator material to achieve heat removal and heat transport inside the heat sink through heat conduction. Since the thermal conductivity of the material depends on the thermal conductivity of the material, and the known thermal conductivity of various materials is not very high, the thermal resistance and thermal resistance of heat transport of the profile radiator are very large. Although the LED heat pipe radiator that appears on the market is reduced to a certain extent compared with the profile radiator, the thermal resistance and thermal transport thermal resistance of the profile heat sink are reduced to a certain extent, but due to the limitation of its heat extraction capacity and the various heat transport limits caused by the internal structure, the thermal resistance value is still large, and it is difficult to achieve timely heat extraction and efficient heat transport from the surface of the LED light source with high power and high heat intensity and heat dissipation to the external environment.
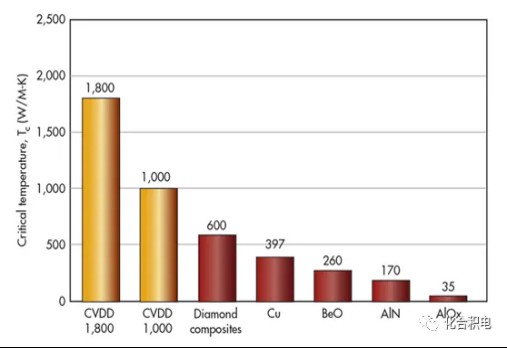
Figure 1 Comparison of the properties of diamond and other heat dissipation materials
Courtesy photo: Metal materials: such as aluminum, copper. The thermal conductivity is 230 W/m.k and 400 W/m.k, respectively, but the thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum and copper is larger, which may cause serious thermal mismatch problems. The coefficient of thermal expansion of Al2O3 (7.2×10-6/°C) and dielectric constant (9.7) are high relative to Si single crystals, and the thermal conductivity (15-35W/ (m·K)) is still not high enough, resulting in Al2O3 ceramics are not suitable for use in high-frequency, high-power electronic devices; Beryllium oxide is more expensive to produce and highly toxic; The thermal conductivity of SiC ceramics is very high, and the higher the purity of SiC crystallization, the greater the thermal conductivity; The biggest disadvantage of SiC is that the dielectric constant is too high, and the dielectric strength is low, which limits its high-frequency application and is only suitable for low-density thermal packaging; AlN material has excellent dielectric properties, stable chemical properties, especially its thermal expansion coefficient and silicon matching and other characteristics make it possible to be a promising semiconductor packaging substrate heat dissipation material, but the thermal conductivity is currently the highest can only be 260W / (m·K), with the LED chip integration and power increases, AlN material also has a certain bottleneck of development. Diamond is the most known material in nature, CVD diamond thermal conductivity can be as high as 2000 W / (m.K), thermal expansion coefficient of about 1.1×10-6 (/°C). Make it the ideal heat dissipation material for high power LEDs.
CSMH focus on high-quality diamond materials and devices research and development, production and sales, the existing core products diamond wafer, diamond hot sedimentation sheet, diamond-based gallium nitride epitaxial wafer, diamond-based aluminum nitride film, etc. Wafer-level diamond growth surface surface roughness Ra<1nm; The thermal conductivity of diamond thermal immersion sheet is as high as 1000-2000W/m.k, and the technical indicators have reached the world's leading level. High-power semiconductor lasers using diamond heat sink (heat sink) are used in optical communication, laser diodes, power transistors, electronic packaging materials, etc.; As an industry role model, we are committed to providing our customers with the most comprehensive diamond thermal management solutions.

Figure 2 High-quality wafer-grade diamonds produced by CSMH
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message