Semiconductor lasers have the advantages of high electro-optical conversion efficiency, small size, strong adjustability and ease of use, and are widely used in solid-state laser pumping, material processing, medical beauty and military defense and many other fields. However, with the maturity of semiconductor laser manufacturing process, especially high-power and small-volume devices, reliability has become an important factor restricting its development. High-power semiconductor lasers will produce a huge heat flux on a small area, especially under the continuous wave (CW) drive, local thermal sniping causes the temperature of the active region to increase with the increase of current, so that the electro-optical conversion efficiency decreases with the temperature increase index, and even causes catastrophic optical damage on the cavity surface, which seriously inhibits the reliability and service life of the device. For semiconductor lasers, the most important problem that cannot be ignored at present is how to make it work in a safe and suitable environment, so the heat dissipation of semiconductor lasers cannot be delayed.
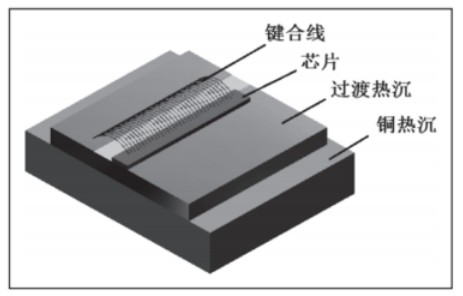
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of a high-power semiconductor structure
For the selection of heat sinking materials:
1. Ceramic materials: such as aluminum nitride, beryllium oxide, alumina. The thermal conductivity is 170-230W/m.k, 190 W/m.k, 20 W/m.k, respectively, of which the impurities and defects generated by aluminum nitride in the sintering process cause the thermal conductivity of the actual product to be lower than the theoretical value, the production cost of beryllium oxide is high and highly toxic, the thermal conductivity of alumina is the lowest and the thermal expansion coefficient of Al2O3 (7.2×10-6/°C) and dielectric constant (9.7) are relatively high compared to Si single crystals, resulting in Al2O3 ceramic substrates are not suitable for use in high-power semiconductor devices.
2. Metal materials: such as aluminum, copper. The thermal conductivity is 230 W/m.k and 400 W/m.k, respectively, but the thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum and copper is larger, which may cause serious thermal mismatch problems. Moreover, the conductor properties of copper and aluminum can lead to electrochemical corrosion in the water-cooled hot and submerged channel, resulting in clogging.
3. Composites: such as aluminum silicon carbide. It is a metal matrix composite that combines SiC ceramics and metal Al with a thermal conductivity of 200 W/m.k, which needs to be increased commissioning costs by changing the content of SiC to match the coefficient of thermal expansion of adjacent materials. The biggest disadvantage of SiC is that the dielectric constant is too high and the dielectric strength is low, which limits its high-frequency application.
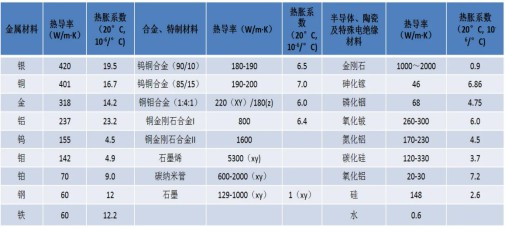
Figure 2 Comparison of the properties of diamond and other heat-sinking materials
In summary, diamond has the highest thermal conductivity at room temperature, which is 5 times that of copper and silver, and it is a good insulator, because it is good
It is an ideal heat dissipation material for high-power laser devices, microwave devices, and highly integrated electronic devices. In the thermal conductivity requirements between 1000 ~ 2000W/m.k, diamond is the preferred and only optional hot sinking material.
CSMH focuses on the research and development and production of diamond, with MPCVD equipment design capabilities, the first in China to master the core process of MPCVD preparation of high-quality diamond and achieve mass production, and the original plasma-assisted polishing of diamond atomic-level surface efficient precision processing method, diamond wafer Ra < 1nm, diamond hot sinks thermal conductivity 1000-2000W/m.k, there are GaN on diamond, Diamond on GaN, diamond-based aluminum nitride and other products. At present, high-power semiconductor lasers using diamond heat sinking have been used for optical communications, and have also been used in RF power amplifiers, laser diodes, power transistors, electronic packaging materials and other fields. In the future, we will continue to improve product quality, benchmark international advanced management level, and continuously improve our products and services through intelligent manufacturing and optimization of production processes.
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message