Pos:
Home KnowledgeTechnologyNumerical Analysis of the Influence of Diamond Composite Materials on the Performance of High-Power LEDsWith the increasing maturity of chip technology, the input power of a single LED chip has gradually increased from 1W to 5W or even higher. Various thermal effects caused by temperature rise will seriously affect the service life and reliability of LED devices. Therefore, effectively dissipating the heat accumulation of LEDs has become increasingly important.
The heat generated by high-power LED chips is mainly conducted to the outer surface through solder, heat sinks, and substrates via heat conduction. Then, the heat on the outer surface is dissipated through various channels and media via thermal convection. Compared with other solid-state semiconductor devices, LED devices are more sensitive to temperature. Junction temperature is an important indicator for measuring the heat dissipation performance of LED packages. Due to the limitation of the chip’s operating temperature, the chip junction temperature can only be kept below 120°C.
The breakthrough to solve the heat dissipation problem of high-power LEDs lies in the design of chip heat sink, scaffold materials, and package structure. Using materials with high thermal conductivity as heat sink materials and substrate materials can accelerate heat conduction. As a representative of the fourth-generation high thermal conductivity materials, diamond/copper composites have extremely high thermal conductivity. Using this material as a heat sink material to replace the traditional copper material plays a certain role in reducing the junction temperature of the chip.
To fundamentally solve the heat dissipation problem of high-power LEDs, the key is to obtain the temperature field distribution of the entire package entity. This can guide the thermal design of the device and ensure that the heat in the junction area is effectively dissipated through components such as the chip heat sink. The external temperature field of the package can be measured through experimental methods, while the internal temperature field can only be obtained through numerical simulation methods.
This work used the finite element method to calculate the temperature field distribution and chip junction temperature of single-chip high-power LEDs. Two types of heat sinks—diamond/copper composites and copper—were used for comparison. Meanwhile, the temperature field distribution and chip junction temperature of high-power LEDs with different heat dissipation structures were calculated when diamond/copper composites were used as the heat sink material.
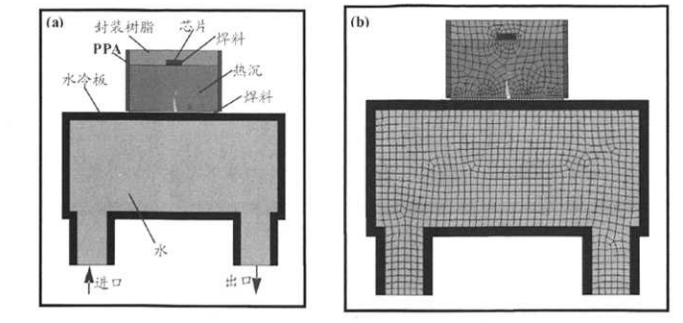
Based on the actual single-chip high-power LED, 2D models of water-cooled heat dissipation structures for 5W and 20W single-chip LEDs were established. The set boundary conditions are as follows:
Ambient air temperature: 25°C;
Convective heat transfer coefficient: 10W/(m²·K);
Inlet water temperature: 15°C;
Water flow rate: 1 m/s;
Outlet pressure: 0 Pa.
This structure was used to study the performance of 5W and 20W single-chip high-power LEDs when diamond/copper composites and copper were respectively used as heat sink materials.
Establishment of 1W Single-Chip LED Models (for Structural Comparison)
To study the performance of single-chip LEDs with diamond/copper composite heat sinks and different heat dissipation structures, 2D models of 1W single-chip LEDs with water-cooled heat dissipation and fin heat dissipation were established respectively (as shown in Figure 2). The LEDs adopted the same structure and materials; the water-cooled part and the fin part had the same length and height; the fins and the water-cooled plate were made of the same aluminum alloy material.
The boundary conditions for fin heat dissipation are:
Ambient air temperature: 25°C;
Convective heat transfer coefficient: 10W/(m²·K).
The boundary conditions for water-cooled heat dissipation are the same as those for the water-cooled heat dissipation structures of 5W and 20W single-chip LEDs.
This study investigates the influence of heat sink materials on the heat dissipation performance of single-chip 5W and 20W LEDs, which share the same water block heat dissipation structure. The heat sink materials used are traditional copper heat sinks and new diamond/copper composite heat sinks.
From the calculation results of the temperature field of LEDs with traditional copper heat sinks, it can be seen that whether the power is 5W or 20W, the temperature field distribution shows the same trend: the temperature at the chip is the highest, and it gradually decreases as the distance from the chip increases, with the water-cooled part having the lowest temperature. The junction temperatures of the 5W and 20W LED chips (with copper heat sinks) are not provided in the original text.
The calculation results of the temperature field of the water-cooled heat dissipation structure for 5W and 20W LEDs using diamond/copper composites as heat sinks are shown in Figure 4. Compared with LEDs using copper heat sinks, they have the same temperature field distribution trend. The difference is that regardless of whether the power is 5W or 20W, the LEDs with diamond/copper composite heat sinks have lower chip junction temperatures, which are 45.8°C and 138.2°C respectively. The junction temperatures are reduced by 4.6°C and 19.1°C, with a reduction rate of 9% and 12% respectively.
The results indicate that diamond/copper composite materials have a relatively obvious effect on reducing the junction temperature of LED chips. Moreover, the higher the input power of the LED chip, the greater the role of the diamond/copper composite heat sink in the heat dissipation of LEDs.
CSMH uses the MPCVD method to prepare large-sized and high-quality diamonds,and currently has mature products such as diamond heat sinks, diamond wafers, diamond windows,diamond composite materials,etc.Among them,the thermal conductivity of diamond heat sinks is 1000-2200w/(m.k), and the surface roughness of diamond wafer a<1nm.It has been applied in aerospace, high-power semiconductor lasers, optical communication, chip heat dissipation, nuclear fusion and other fields.
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message