IGBT is a new type of semiconductor device, as the mainstream of new power semiconductor devices, whether in the industry, communications, 3C electronics and other traditional fields, or rail transit, new energy, smart grid, new energy vehicles and other strategic emerging industries, IGBT plays a vital role. But also inseparable from the thermal characteristics, the weakness of the power semiconductor module is overvoltage overheating, 10 °C rule shows that: every 10 °C reduction in the device temperature, reliability increased by 1 times, the current due to IGBT due to thermal runaway and lead to failure of the phenomenon is the most common, it can be said that most of the IGBT power semiconductor module failure reasons are related to heat, therefore, reliable thermal management is to ensure the long-term use of IGBT top priority.
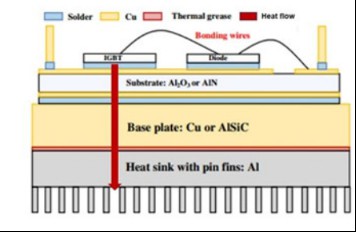
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of IGBT structure
The materials commonly used for IGBT heat dissipation are:
1.Graphene: The advantage of graphene for IGBT is that the transverse conductivity is high, and the disadvantage is that the graphene sheet with poor thermal conductivity in the C axis direction and the thicker graphene sheet will drop the toner, resulting in a short circuit in the electrical appliances. In addition, the heat dissipation of IGBT is a systems engineering, and graphene is used for different parts/parts (Chip, DCB, BasePlate, heat sink and the interface of these parts) The role is different, and the requirements for graphene are also different. If used as an interface, graphene needs to be compounded into existing interface material formulations or redesigned formulations. The process is complex and requires targeted development.
2.Ceramic series: Thermal conductive ceramic sheet is mainly AI2O3, an electronic ceramic material that has been roasted and molded at high temperature, mainly used for high-power power supply equipment, IGBT modules, ICMOS tubes, etc. Advantages: thermal conductivity up to 25W, can withstand high temperature above 1600 °C, high insulation properties and mechanical strength. Disadvantages: high surface hardness, can not fully fit between the heat source and the heat sink, the need for thermal grease auxiliary talent to stop heat conduction work, product cost is higher.
3.Phase change material series
Phase change material is through the material heat storage, the heat is absorbed into the material inside, while the material due to the sheet softening into an inactive elastomer, can effectively reduce the thermal resistance between the heat source and the heat sink, aggravate the heat transfer process; Typically used in high-frequency processors, IGBT modules, cache chips, notebook computers and other electronic devices. Advantages: at room temperature, it is flake-like, and at high temperature, the attack phase becomes semi-liquid, reducing the thermal resistance and accelerating the heat transfer work, and it has strong heat absorption talent in the process of phase change. Disadvantages: The material cost is higher, the performance drops after more circulating heat storage and exothermic, and the compatibility with other materials is poor.
4.As the hardest material known in the world, diamond has excellent properties such as large band gap width, extremely high thermal conductivity, high electron saturation drift speed, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, radiation resistance, etc., and has extremely important application prospects in the fields of high voltage and high efficiency power electronics, high frequency and high power microelectronics, and deep ultraviolet optoelectronics. Diamond thermal implants have the highest known thermal conductivity (2200W/(m·K)) of natural matter, 4 times larger than silicon carbide (SiC), 13 times larger than silicon (Si), 43 times larger than arsenic crops (GaAs), and 4 to 5 times larger than copper and silver.
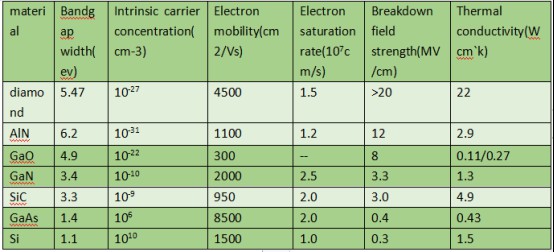
Figure 2 Comparison of the properties of diamond with other materials
In summary, for the thermal management problem of IGBT, the ultra-high thermal conductivity of diamond (about 2000W/m.k) and the extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion combine various factors such as cost and heat dissipation effect. In the end, diamond wafer is the most ideal IGBT heat dissipation material. In summary, for the thermal management problem of IGBT, the ultra-high thermal conductivity of diamond (about 2000W/m.k) and the extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion combine various factors such as cost and heat dissipation effect. In the end, diamond is the most ideal IGBT heat dissipation material.

Figure 3 High-quality wafer-grade diamonds produced by CSMH
CSMH focus on the production and preparation and sales of high-quality diamond, diamond wafer growth surface surface roughness Ra<1nm, diamond thermal implant thermal conductivity of 1000-2000W/m.K, technical indicators have reached the world's leading level. High-power semiconductor lasers using diamond heat sinking have been used for optical communication, and are also used in laser diodes, power transistors, electronic packaging materials and other fields. As a company focusing on diamond production and research and development, we will provide you with the most thoughtful thermal management solutions.
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message