Pos:
Home KnowledgeTechnologyDiamond wafers assist in efficient heat dissipation of semiconductor devicesWith the development of semiconductor devices towards integration and miniaturization, the power density of integrated circuits continues to increase,with hotspots reaching up to 1000W/cm2, the continuous accumulation of heat poses a threat to the performance, stability, and lifespan of electrons. Therefore, improving the heat dissipation capacity of electronic devices is crucial. Diamond material, known as the fourth generation heat dissipation material, is a key heat dissipation material for high-power electronic devices, semiconductor chips, 5G communication, T/R modules and other devices.
CSMH uses microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) to prepare large-sized and high-quality diamond wafers. This method has advantages such as no pollution of microwave energy and pure gas raw materials, making it the most promising technology for preparing large-sized and high-quality polycrystalline diamonds.
There are two main methods for the application of diamond and semiconductor devices: direct deposition and bonding. Electrochemical deposition (CVD) adopts a low-temperature bonding method. At room temperature, the surface activation method is used to transfer the epitaxial GaN layer grown on a Si substrate to a diamond substrate, obtaining a GaN on diamond heterojunction bonding structure with interface thermal conductivity comparable to that prepared by epitaxial growth method.
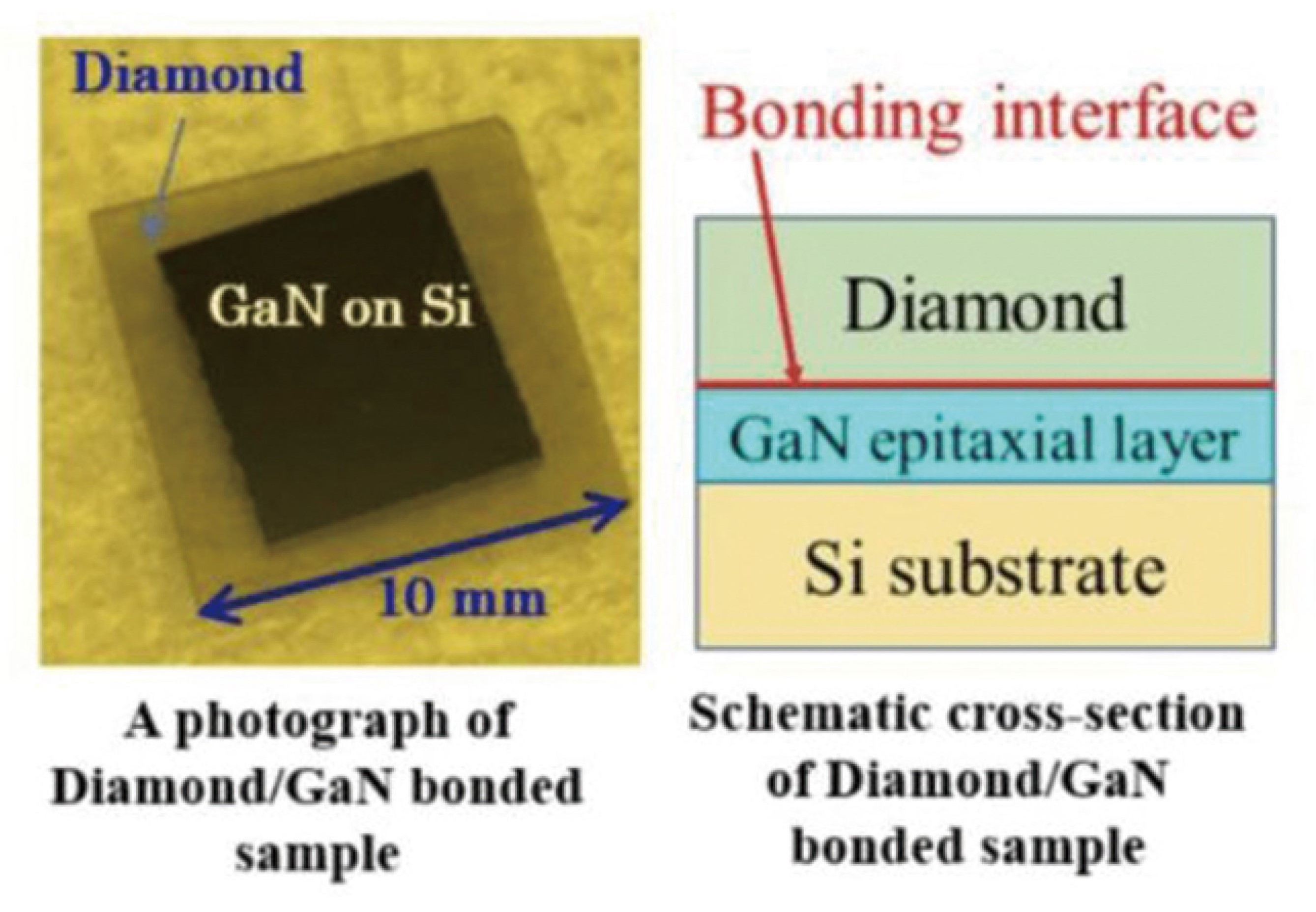
Diamond/GaN junctions fabricated
Diamond is used as a heat sink material in semiconductor lasers, and Ti/Pt/Au multilayer films are deposited on the surface of CVD diamond heat sinks through a magnetron sputtering system as a metallized layer. A 10um thick In film was deposited through an electron beam evaporation system as a solder layer for semiconductor laser packaging. Using a high-precision mounting machine, a semiconductor laser linear array is mounted on the surface of a diamond heat sink using a COS (chip on mount) structure, and then onto a copper based water-cooled heat sink.
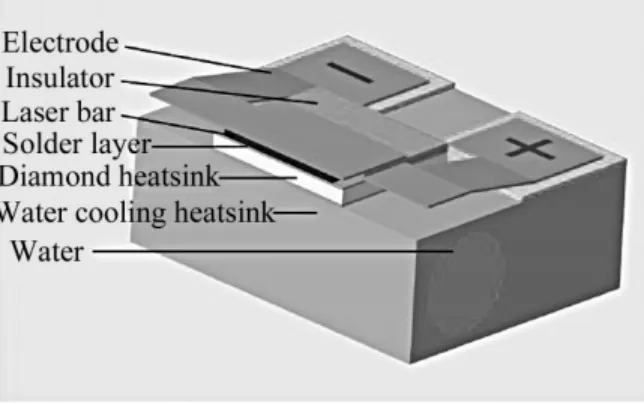
Diamond as a heat sink material in semiconductor lasers
Diamond materials have unique physical and chemical properties, such as high thermal conductivity, high wear resistance, and high chemical stability. Based on the characteristics of diamond, CSMH has launched diamond heat dissipation solutions for semiconductor devices, helping to improve the reliability and stability of devices and solve the problem of chip jamming. Its core products include diamond heat sinks, diamond wafers, diamond windows, and diamond heterojunction integrated composite substrates. Currently, they have been applied in high-power semiconductor devices, drones, aerospace, new energy vehicles, and medical devices.
 闽ICP备2021005558号-1
闽ICP备2021005558号-1Leave A Message